What are Prepositions?
Prepositions are defined as words that show the relationship in a sentence. Various Types of Preposition tells us about direction, location, and time. Prepositions exhibit the relationship between subject, object, or ideas. Prepositions provide context and clarity in sentences. Here are some examples:
Examples of Prepositions:
- On
- Beside
- In
- Between
- In front of
- Under
- Above
- Near
- Through
- Over
- Against
- With
- Among
- Behind
- Below
- Across
- Around
- Inside
- Outside
- Towards
Use of Preposition in sentences:
- I met her in the park. (in)
- The sparrow is sitting on the wall. (on)
- The note is under the mat. (under)
- The basket is placed over the bed. (over)
- She sits besides her cousin in class. (beside)
- The secret rests between both of us. (between)
- Ali parked the car behind the office. (behind)
- The kids are playing in front of their school. (in front of)
- There’s a cafe near my university. (near)
- She feels comfortable among her friends. (among)
- Put the sticky notes inside the book-rack. (pen)
- They started running towards the university. (towards)
- I would love to have coffee with chocolate cake. (with)
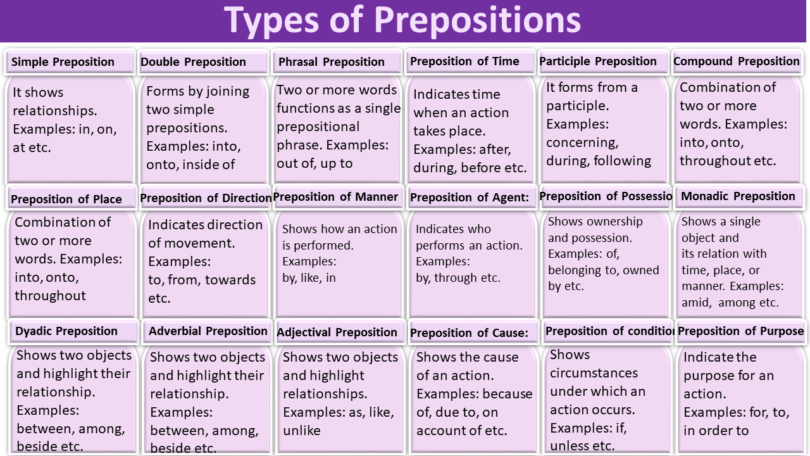
Types of Preposition:
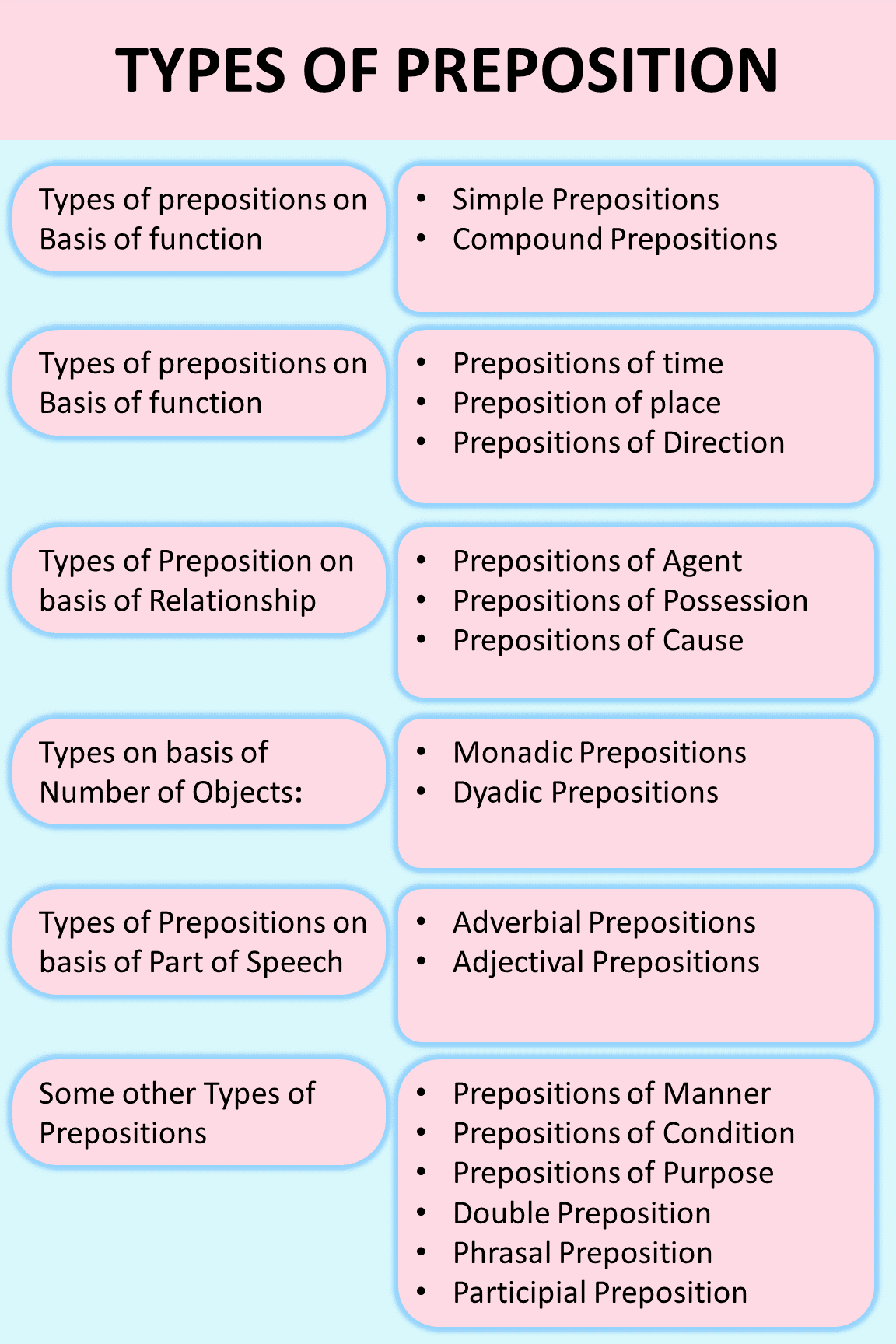
In the realm of language, prepositions can be classified on the basis of different criterias. We can classify prepositions on the basis of their functions, relationship and uses. A lot of times, you’ll read, there are five types of prepositions. They are:
- Simple preposition
- Compound preposition
- Double preposition
- Phrase preposition
- Participle preposition
But, do you know how many ways we can classify prepositions? Now, you’ll really do, after reading this blog.
Here are Types of Preposition on basis of Function:
- Simple Prepositions
- Compound Prepositions
Following are Types of Preposition on basis of uses:
- Prepositions of time
- Preposition of place
- Prepositions of Direction
Types of Preposition on basis of Relationship:
- Prepositions of Agent
- Prepositions of Possession
- Prepositions of Cause
Classification of Preposition on basis of Number of Objects:
- Monadic Prepositions
- Dyadic Prepositions
Here are Types of Preposition on basis of Part of Speech
- Adverbial Prepositions
- Adjectival Prepositions
Prepositions are not just limited to the above types, as:
- Prepositions of Manner: e.g., by, like, with.
- Prepositions of Condition: e.g., in, on.
- Prepositions of Purpose: e.g., for, to.
Preposition and its Types
The Most Common Prepositions:
The most common prepositions represent prepositions that are frequently used. They are called simple prepositions. The most common prepositions are:
- Of
- At
- With
- Into
- From
- Including
- During
- Against
- Until
Types of Preposition with Definition and Examples
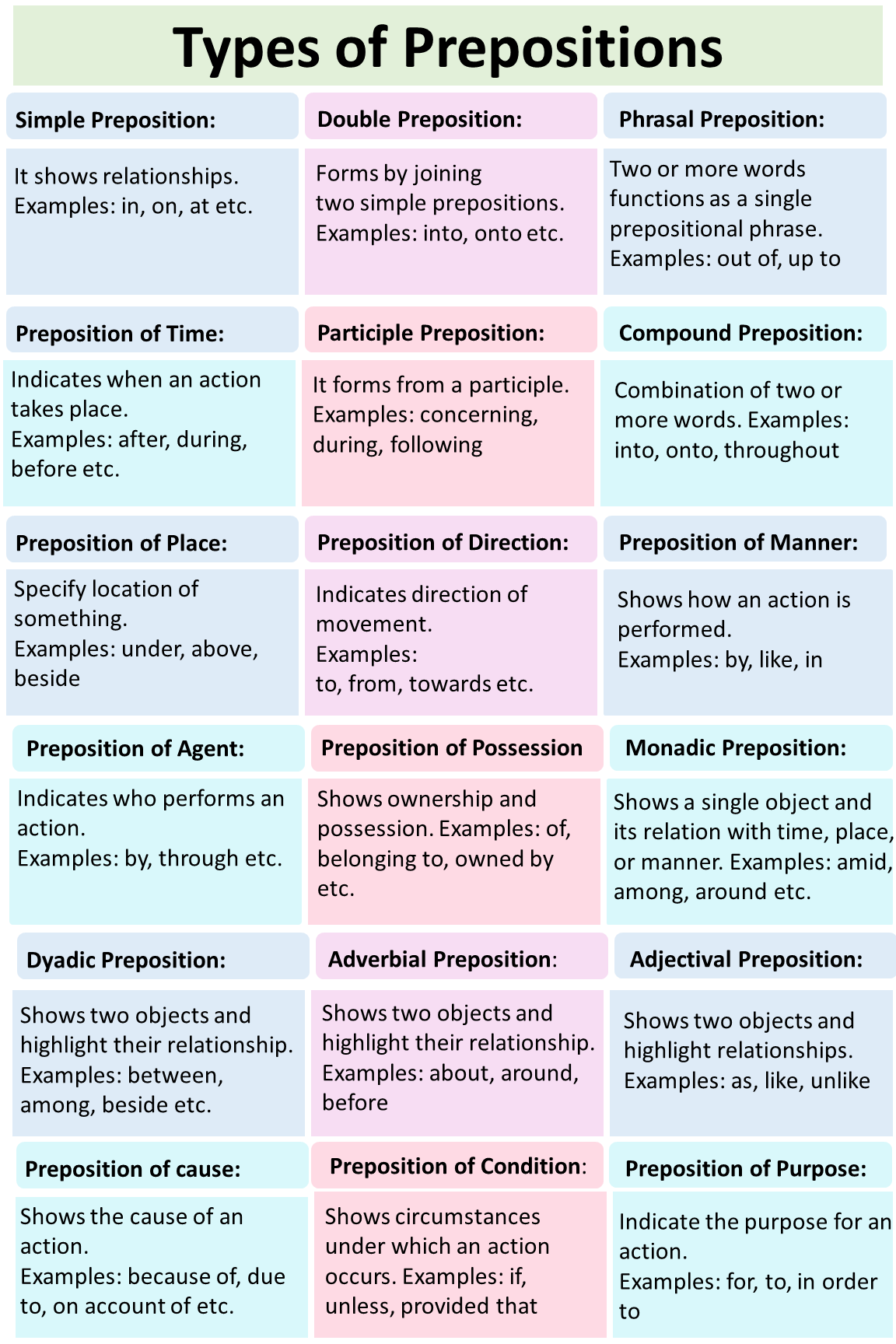
Simple Prepositions:
It is a single word which shows the relationship between objects. Simple prepositions play an important role to exhibit spatial, directional and temporal relationships. They are vital to form prepositional phrases, prepositional phrases give additional information about the direction, location, or time.
Examples:
- In
- On
- Under
- Over
- At
- By
- With
- Through
What is a Double Preposition?
Double Preposition is formed by combining two simple prepositions
Examples include
- According to
- On top of
- In addition to
- Because of
- In front of
- Up to
- Out of
- In between
- As of
- In spite of
- By means of
- Apart from
- With regard to
- With respect to
- Due to
What is a Compound Preposition?
Compound prepositions are very similar to Double prepositions. Have you noticed that both are two-word phrases? The double preposition is formed by combining two simple prepositions and compound preposition is formed by joining simple preposition and a non-prepositional word.
Example of Compound Prepositions:
- according to
- along with
- ahead of
- alongside of
- apart from
- as against as
- between as
- around about
- compared with
- as compared to
- at that point
- in time
- as for
- at this point
- in time
- at the time of
- because of
- at the point of
- by force of
- by reason of
- by virtue of
- by means of
- due to
- during the course of
- by way of
- for fear of
- except for
- for lack of
- for the reason that
- from above
- for the sake of
- for the purpose of
- from between
- from among
- view of
- from behind
- in compliance with
- in close connection with
- from beneath
- from the point of
- in connection with
- in a manner
- in case of
- in accordance with
- similar to
- in care of
- in comparison to
- in common with
- on the basis of
- on the point of
- on top of
- prior to
- on the part of
- outside of
- on account of
- previous to
- short of
- owing to
- on behalf of
- regardless of
- pursuant to
- relative to
- relating to
- out of similar to
Classification of Preposition on basis of uses:
Prepositions of time
Prepositions of time indicate the time of an action or event. These help provide temporal context. Examples are as:
- She has a class at 7 PM.
- We will go to Switzerland in summer.
Preposition of place
Prepositions of place shows position or location of an object, person or event. Some common examples are:
- The pencil is in the box.
- The sugar pot is on the table.
Prepositions of Direction
Prepositions of direction indicate the movement or path in relation to other elements in a sentence. They provide information about motion or position. Here are some common examples:
- They walked to the market.
- The kids are walking towards the park.
- She jumped off the table.
Here are Types of Preposition on basis of Relationship:
Prepositions of Agent
Prepositions of agent indicate who is doing work or action. They express the agent for a particular action. Some common examples include:
- The novel was written by a famous writer.
- The cake was baked by my sister.
Prepositions of Possession
Prepositions of possession show ownership between two elements. Here are some common examples:
- The colour of the pencil is blue.
- The notebook belongs to Aira.
- The land is owned by the Mr. John.
Prepositions of Cause
Prepositions of cause indicate the reason or cause and express factors for an outcome. Here are some common prepositions of cause along with definitions and examples:
- The class was postponed because of heavy rain.
- The flight was cancelled due to some technical issues.
- We succeed, thanks to our teamwork.
Following are Types of Preposition on basis of Number of Objects:
Monadic Prepositions:
These prepositions show a single object in a sentence, relate the subject to time, place, or manner.
- Example: He sat in the street.
Dyadic Prepositions:
Dyadic prepositions govern two objects and highlight the relationship between both.
- Example: The over-bridge connects two roads.
Types of Preposition on the Basis of Part of Speech:
Adverbial Prepositions:
They function as adverbs, modify verbs and describe action.
- Example: He walked in fastly.
Adjectival Prepositions:
They function as adjectives, modify nouns and add details about the subject.
- Examples: The girl with the pink dress is my friend.
Additional Categories of Prepositions:
Prepositions of Manner:
They show how an action is performed, shows method or style.
- Example: The artist painted the pot with great skill.
Prepositions of Condition:
Preposition of condition shows the state of an action.
- Example: We succeeded with our team work, hard work and dedication.
Prepositions of Purpose:
Prepositions of purpose highlight the reason behind an action, they give reason for an activity.
- Example: They went to the Fortress for a 9-D Ride.
Phrasal Preposition:
Two or more words functions as a single prepositional phrase.
- Example: He sat down in front of the TV.
Participle Preposition:
It forms from a participle.
- Example: During the meeting, she took notes.
In conclusion, prepositions offer clarity and depth to language and play a vital role in constructing right sentences.
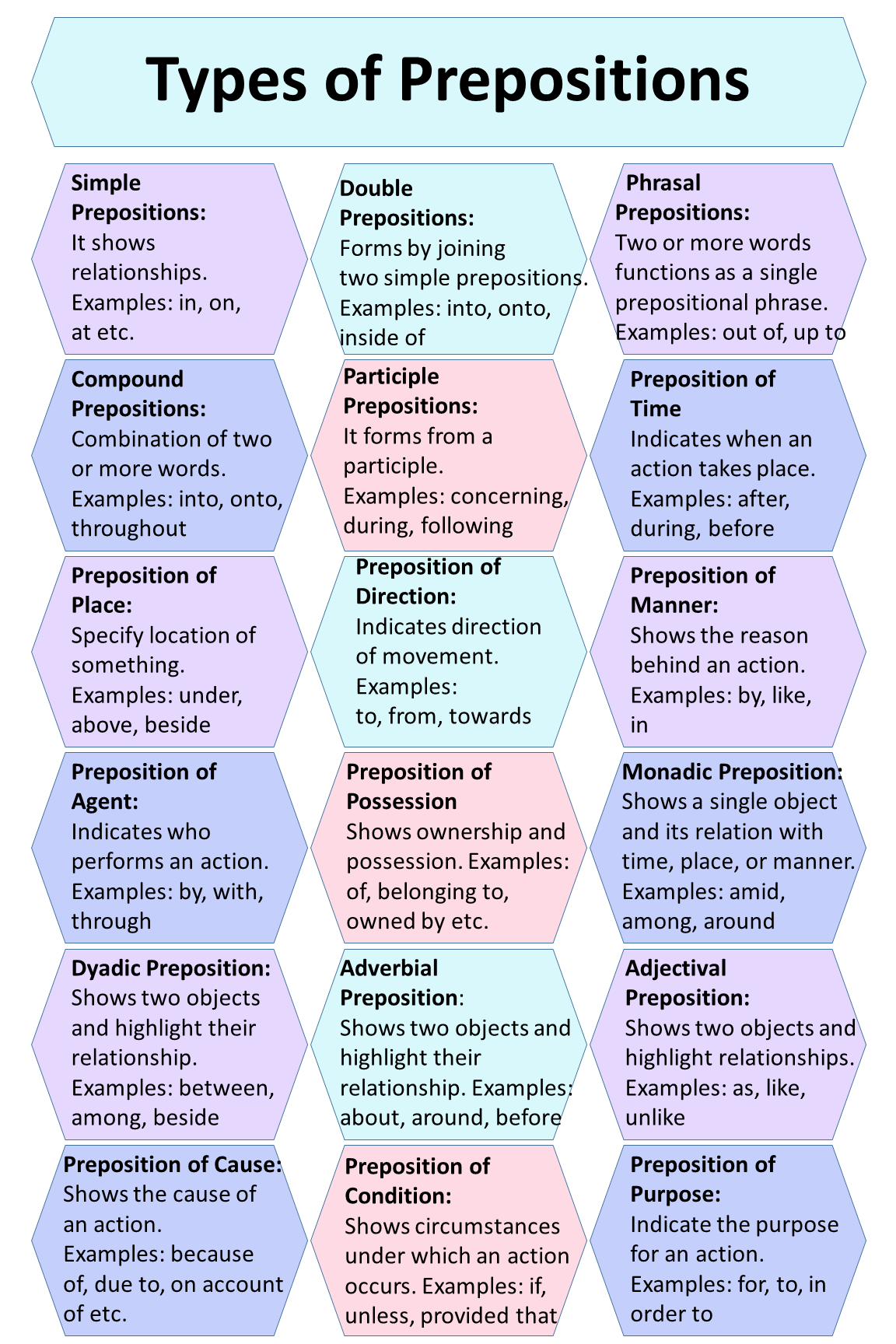
Tabular Representation of Types of Preposition:
| Sr. no | Type | Description | Examples |
| 1 | Simple Prepositions: | It shows relationships. | In, on, at etc. |
| 2 | Compound Prepositions | Combination of two or more words. | Into, onto, throughout |
| 3 | Prepositions of Time: | Indicates time when an action takes place. | After, during, before |
| 4 | Prepositions of Place: | Specify location of something. | Under, above, beside |
| 5 | Prepositions of Direction | Indicates the direction of movement. | To, from, towards |
| 6 | Prepositions of Agent | Indicates who performs an action. | By, with, through |
| 7 | Preposition of Possession | Shows ownership between two elements. | Of, belonging to, owned by |
| 8 | Preposition of Cause | Indicates cause of an action. | Because of, due to, on account of |
| 9 | Monadic Preposition | Shows a single object, relate the subject to time, place, or manner. | Amid, among, around |
| 10 | Dyadic Preposition | Shows two objects and highlight their relationship. | Between, among, beside |
| 11 | Adverbial Preposition | It functions as adverbs and modify verbs. | About, around, before |
| 12 | Adjectival Preposition | Function as adjective and modify nouns | As, like, unlike |
| 13 | Prepositions of Manner | Describes how an action is performed. | By, like, in |
| 14 | Prepositions of Condition: | Shows circumstances under which an action occurs. | If, unless, provided that |
| 15 | Prepositions of Purpose | Indicate the purpose for an action. | For, to, in order to |
| 16 | Double Preposition | Forms by combining two simple prepositions | Into, onto, inside of |
| 17 | Phrasal Preposition | Two or more words functions as a single prepositional phrase | Out of, up to, in between |
| 18 | Participle Preposition | It forms from a participle. | Concerning, during, following |
Preposition and its types