A creative way to learn Verbs and Types of Verbs. Learn Verbs and their types to improve your language.
Here is a story to explore Types of Verbs, with Definitions and Examples. Once in the linguistic tapestry, I, along with five friends of mine, eagerly onboarded a journey of exploration. It was a joyous experience graced by delightful weather. The air carried a gentle breeze that whispered promises of knowledge and adventure. The sun played hide-and-seek with fluffy clouds.
With every moment, it became clear that this journey isn’t just about exploration, but to uncover the magic hidden within the twists and turns of language. Our collective curiosity became the driving force to the twelve captivating stops of this extraordinary expedition. Each person brought their unique perspective and storytelling flair, creating a dynamic ensemble that added depth and richness to the unfolding narrative.
While we had just started the journey, we met a person named Alex, who is 65 years old, and has a lot of knowledge about verbs. He told us that once in a distant era, verbs emerged as the genuine architects of expression. These dynamic entities infused vitality into sentences, crafting vibrant images and forging connections between words.
Mr. Alex was a treasure of knowledge and a living library for us due to his vast experience and exploration. His eyes were lightning up with stories, and he was like a living library. We asked him about a lot of things and he told us a lot, in very interesting tales. Talking to him was like going on a journey through experiences. He shared wisdom with a beautiful smile. In a world full of quick information, he’s a reminder that there’s something special about a lifetime of learning.

Verbs, its Definition and Types
Stop 1: The Action Verbs, Types of Verbs that Brings Sense to Life:
The first stop of our journey was quite interesting. It was about Action Verbs that bring sense to life. Action verbs are also called dynamic verbs. These are used to express physical or mental actions. These verbs describe actions done by someone or something.Action verbs are used to convey a sense of movement, change, or activity. These are the powerhouses of a sentence, used to drive the narrative forward and describe events. They play an important role in making communication engaging and lively. The thing we love about action verbs is that anyone can visualise the actions taking place, with the help of action verbs.
Examples include “write,” “read,” “dance,” and “eat.”
There are two types of action verbs:
- Transitive Verbs
- Intransitive Verbs
Transitive Verbs
Transitive verbs require a direct object to give meaning to a sentence. These indicate the subject to which action is being done, transferring the action from subject to object. Subject is performing the action on the object.
For Example
- He read an informative book.
- In this sentence, “read” is a transitive verb, and “informative book” is the object on which action is being done.
Intransitive Verbs
Intransitive verbs are a type of action verbs that do not require a direct object. These express actions that do not transfer to object, conveying an idea without additional elements. In the realm of verbs, intransitive verbs are independent. Intransitive verbs express actions without the need of direct object. intransitive verbs set an example of independence and confidence by shining on its own. It shows that action doesn’t require any subject.
Example
- She laughs.
- The verb “laughs” is intransitive and self-contained. It doesn’t need an object to give a complete meaning to a sentence.
Dynamic Verbs are also known as action verbs. These describes actions that can be seen, felt and heard.
Stop 2 Linking Verbs, Types of Verbs that forms Linkage Bridges:
Continuing our journey, we came across a bridge, it was a very adventurous bridge of linking verbs.
There, we found the bridge is made up of linking words, providing the pathway by removing physical barriers and obstacles. Linking verbs connects ideas, ensuring a smooth flow in a sentence. Linking Verbs are defined as words used to connect the subject with a subject complement, that could be an adjective or a noun. They describes relationship between the subject and its other information.
Examples of linking verbs include is, am, are, was, were etc.
Stop 3: The Helping Verbs, Types of Verbs that always Helps:
Unexpectedly, we met a man who was very helpful to all. He was like a gift from God for everyone. He told us that he got his motivation from Helping Verbs.
Helping verbs are also called auxiliary verbs. Helping Verbs assist the main verb in a sentence. They give information about the action that is happening by the main verb. Helping verbs create different aspects, voices, moods, and tenses in sentences.
Examples of helping verbs include Is, must, has, can, are, do, will be, have, had etc.
Stop 4: The Modal Verbs:
Within the fascinating world of verbs, we came across modal verbs. They were magnetic narrators, each with its unique ability and use.
Another term for modal verb is modal auxiliary verbs or modals. They modify the main verb in a sentence. They reflect the speaker’s perspective on the necessity, desirability or likelihood of the action. These verbs introduce a subjective element, to offer insights into intentions, attitude or beliefs, regarding the action being described.
Examples of modal verbs include can, might, may, could, shall, should, will, must, ought to and would.
Modal verbs play an important role in shaping the intention of a sentence, it allows speakers to express certainty, willingness or obligation.
Stop 5: The Stative Verbs:
Stative verbs are verbs that show a state instead of an action. Unlike action verbs, stative verbs describe a state of being, possession, emotion or a sense. Stative verbs convey emotions, thoughts, or qualities that can’t be measured in terms of intensity. They are constant or static. They reflect a state of existence instead of an action.
For example:
- He owns a studio. (owns)
- She loves cooking. (loves)
Stop 6: The Phrasal Verbs:
Phrasal verbs are verbs consists of a main verb and one or more particles, which can be adverbs or prepositions, together to form a semantic unit. These are idiomatic expressions, as single words can’t give their meanings. Phrasal verbs are often used in English and are used to convey relationships, actions, or changes in states.
Examples include break down, Look up and put off etc.
Stop 7: Regular Verbs, Types of Verbs which are Regular:
Regular verbs follow a pattern in past participle and past tense forms. The base form of the verb. Regular ends with “-ed” while creating past and past participle tense.
Examples include:
- Base Form: walk
- Past Tense: walked
- Past Participle: walked
Stop 8: The Irregular Verbs, Irregular Types of Verbs
Verbs that do not follow the regular pattern while forming their past tense or past participle are Irregular Verbs and don’t necessarily end with “ed- form”. Irregular verbs undergo changes to show past actions.
Examples include:
- Base Form: go
- Past Tense: went
- Past Participle: gone
Stop 9: The Gerunds and Infinitives:
We were wondering about -ing forms and base verb forms and came across Gerunds and Infinitives. A verb form that functions as a noun is called gerund. Addition of “-ing” form as a suffix to the base form of a verb forms gerund. Gerund is very important, it functions as subject, object, or complement. Examples include:
- I enjoy writing books. (writing)
- She likes cooking. (cooking)
An infinitive the base form of a verb, by adding “to” before a word. Infinitives can function as nouns, or adverbs or adjectives.
- This is the best book to study.
- She loves to read.
Stop 10: Reflexive Verbs:
Reflexive verbs are types of Verbs which shows the subject performing the action on itself. They are used as the object of the verb and indicate the action is being done to oneself. Examples are yourself, myself, himself, itself, herself, ourselves, themselves and yourselves.
- She cleansed her face before going to bed.
- They taught themselves how to play the cricket.
- She pride herself on being topper.
- They enjoyed themselves at the party last night.
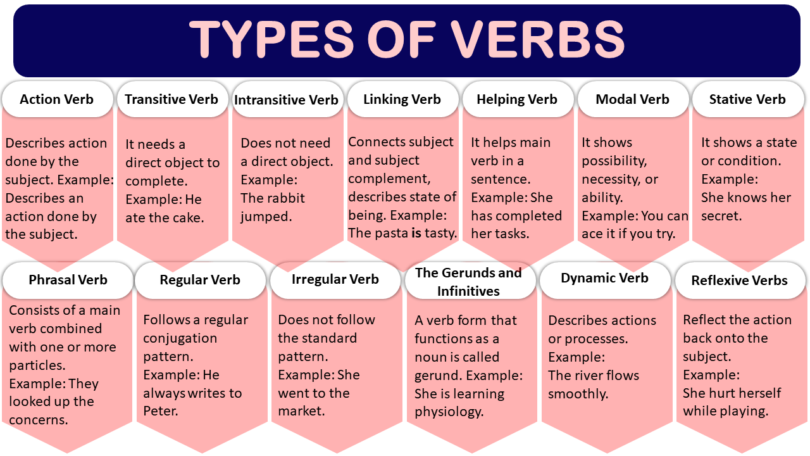
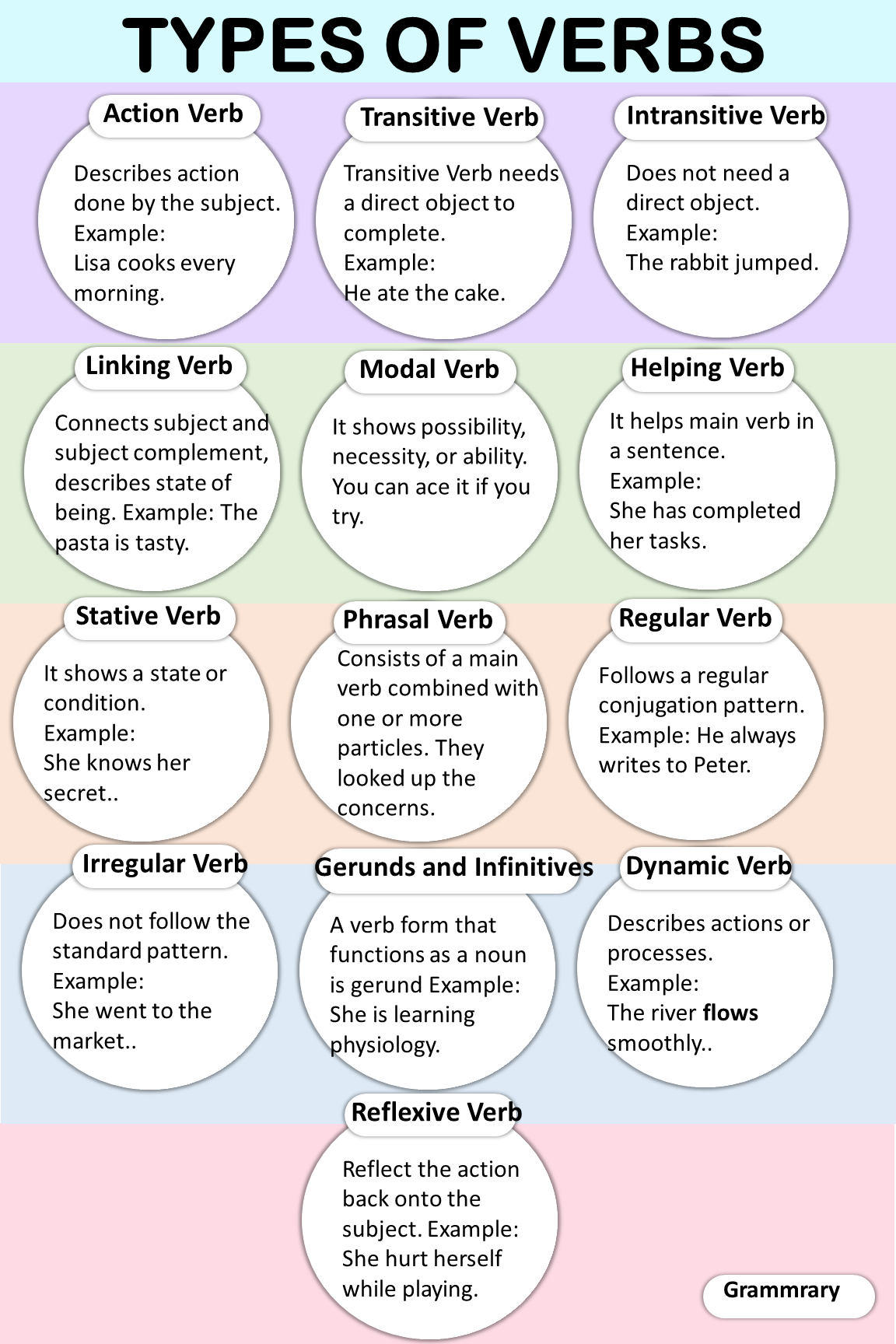
And so, this journey of ours came to an end, leaving us with a treasure of knowledge. In conclusion,. Verbs describe an action, occurrence, or state of being. Verbs play an important role in forming sentences. There are various types of verbs in table below:
Table showing Types of verbs with descriptions and examples:
| Sr no | Types of Verb | Description | Example |
| 1 | Action Verb | Describes an action done by the subject. | Lisa cooks every morning. |
| 2 | Transitive Verb | needs a direct object to complete. | He ate the cake. |
| 3 | Intransitive Verb | Does not need a direct object. | The rabbit jumped. |
| 4 | Linking Verb | Connects the subject and subject complement and describing a state of being. | The pasta is tasty. |
| 5 | Helping Verb | It helps main verb in a sentence. | She has completed her tasks. |
| 6 | Modal Verb | It shows possibility, necessity, or ability. | You can ace it if you try. |
| 7 | Stative Verb | It shows a state or condition. | She knows her secret. |
| 8 | Phrasal Verb | Consists of a main verb combined with one or more particles. | They looked up the concerns. |
| 9 | Regular Verb | Follows a regular conjugation pattern. | He always writes to Peter. |
| 10 | Irregular Verb | Does not follow the standard pattern. | She went to the market. |
| 11 | The Gerunds and Infinitives | A verb form that functions as a noun is called gerund | She is learning physiology. |
| 12 | Dynamic Verb | Describes actions or processes. | The river flows smoothly. |
| 13 | Reflexive Verbs | Reflect the action back onto the subject. | She hurt herself while playing. |
Types of Verbs with Definition and Examples