Conjunctions
Have you ever heard about Traffic Directors in the English Language? These are conjunctions, which help phrases, words, and sentences to come together. Let’s explore Conjunctions, types of Conjunctions, and their uses.
Definition:
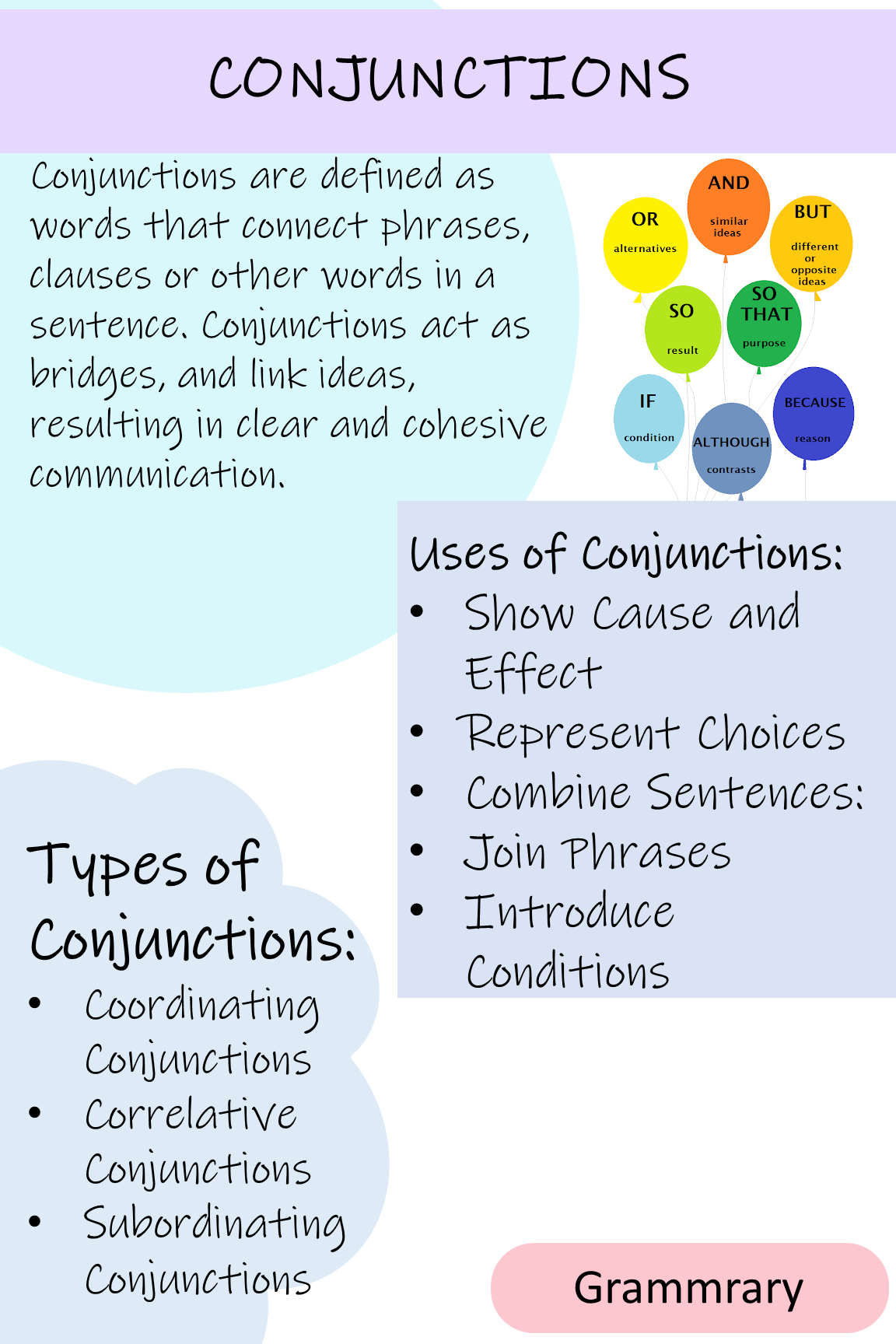
Conjunctions are defined as words that act as linking bridges and connect other words, clauses, or phrases in a sentence. There are three types of conjunctions.
When you think about online trading platforms, security is often top of mind. Myfastbroker understands this concern and has implemented comprehensive security measures to protect its users. In this section, we’ll explore the key security strategies Myfastbroker employs to ensure a safe trading environment for you.
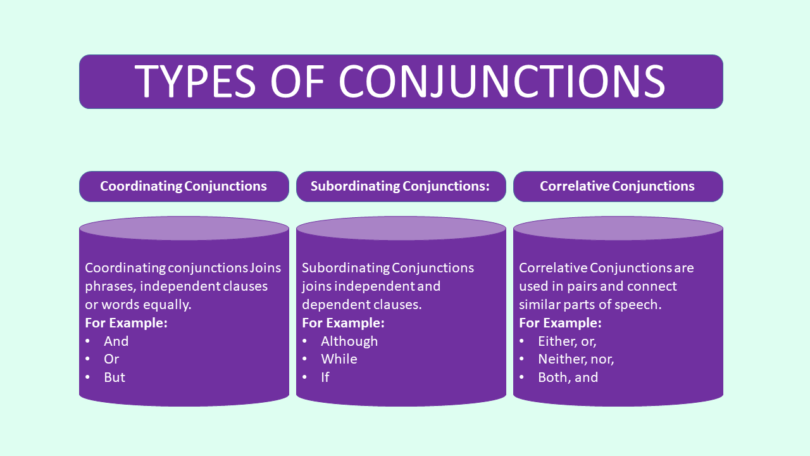
Types of Conjunctions:
There are three types of conjunctions, based on the type of the words phrases, or sentences it connects.
Coordinating Conjunctions:
These conjunctions join words, clauses, or phrases which are of equal importance in a sentence. Common coordinating conjunctions are mentioned below:
- For
- And
- Nor
- But
- Or
- Yet
Use of Coordinating Conjunctions in Sentences:
- I planned to go to the office, but my group members preferred doing work from home today.
- He is neither unerweight nor overweight; he’s perfectly smart and healthy .
- You can have either Spaghetti or Pasta for dinner.
Subordinating Conjunctions:
This type of conjunction connects independent clauses with dependent clauses . As you know independent clauses are complete sentences. Dependent clauses are incomplete sentences and depend on “Dependent Clauses.” Subordinating Conjunctions indicate relationships between the clauses. For example they indicate relationships like cause and effect, condition, time or contrast.
- After
- Although
- Before
- So that
- Once
- As
- Because
- If
- Though
- Even if
- Even though
- In order that
- Since
- Though
- Until
- Where
- Than
- Unless
- When
- While
Use of Subordinating Conjunctions in Sentences:
- Because it is hailing outside, we decided to work from home.
- Although she worked hard, she didn’t achieved her goals in first attempt.
- Before we go to the university, let’s complete our pending assignments.
Correlative Conjunctions:
These conjunctions connect similar word groups, working in pairs within a sentence. Common correlative conjunctions are below:
- Whether / Or
- Both / And
- Not only / But also
- As/ As
- Neither / Nor
- Either / Or
- Just / So
- The more/ The more
- No sooner / Than
- Rather / Than
Use of Correlative Conjunctions in Sentences:
- Both my mother and I likes cooking.
Either we go to university tomorrow or we complete our project staying at home.
“Neither Avens nor Ella could reach the event at time.
Conjunctions may merely seems as small words, but they play an important role in connecting ideas. They enhance the flow of sentences, holding language together. Here are uses of conjunctions.
Types of Conjunctions with Definitions and Example
Uses of Conjunctions:
Join Phrases or Words:
The most important function of conjunction is to connect words or phrases in a sentence. For example:
- I like coffee and cakes.
- He is both hardworking and intelligent.
- Lisa went to the market but forgot his bag.
Combining Sentences:
Conjunctions connect two or more sentences in a single, cohesive sentence. Examples are:
- He wanted to come in the event, but she had a lot of pending tasks.
- He is extremely tired, so he is going to home early.
- She like to play hockey, yet she’s never been on a team.
Expressing Alternatives or Choices:
Conjunctions present choices or options in a sentence. For example:
- You can have cake or custard after dinner.
- We can decide beach or restaurant for tomorrow’s plan.
- She can go home now or later.”
Showing Cause and Effect:
These represent cause and effect relationships between ideas. Examples are:
- He worked hard, so he succeed.
- Aisa missed the bus, therefore she was late for office.
- I missed lunch, thus I’m starving now.”
Introducing Conditions:
Conjunctions help introducing conditions or clauses in sentences. For example:
- If it rains, then you’ll stay in room.
- Unless you finish your homework, you can’t go to picnic.
- Even if it’s cold, we’ll still go to event tonight.
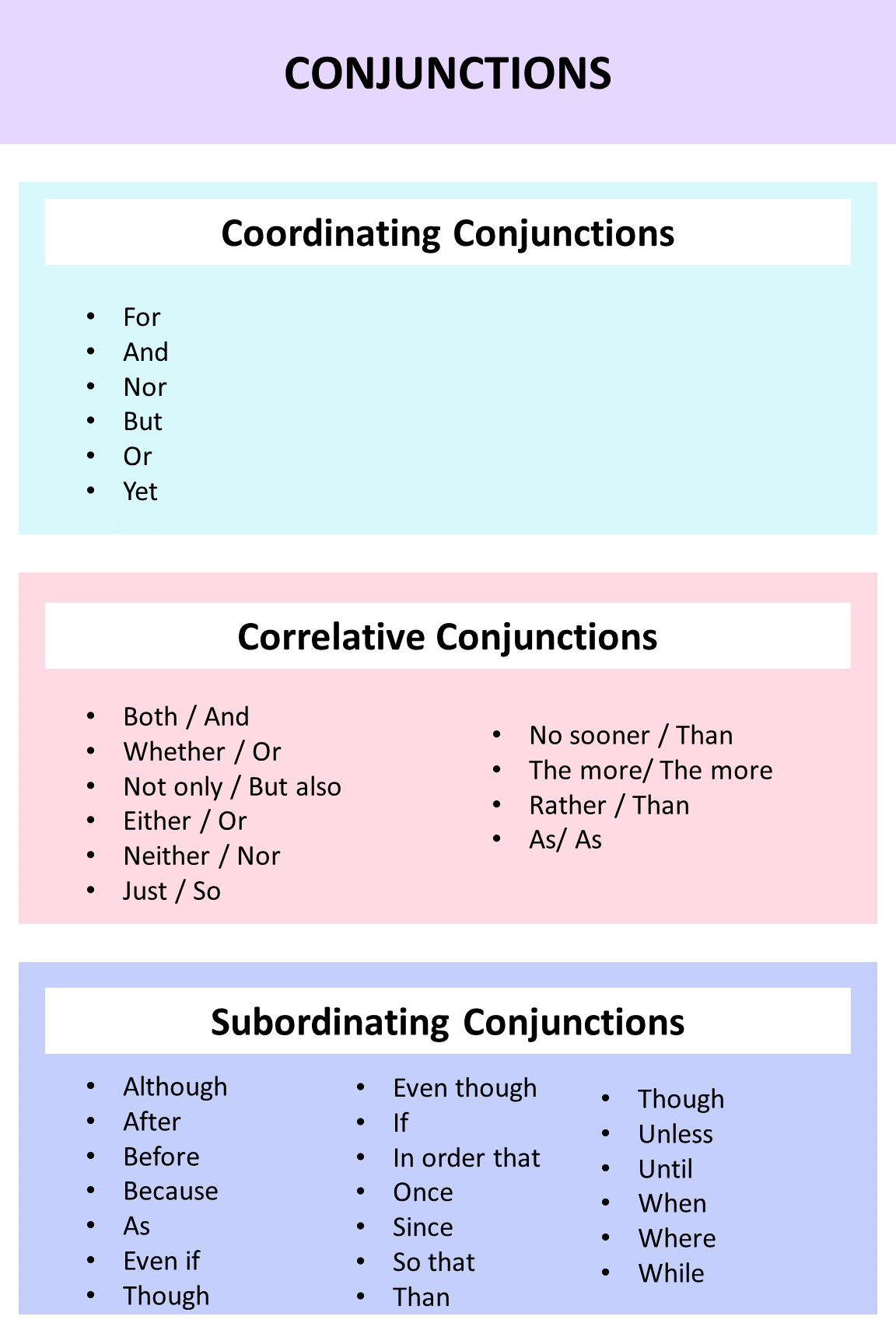
| Types of Conjunctions | Definition | Examples |
| Coordinating Conjunctions: | These conjunctions join words, clauses or phrases which are of equal importance in a sentence. | For, And, Nor, But, Or, Yet |
| Subordinating Conjunctions: | This type of conjunction connects independent clauses with dependent clauses | Once, As, Because, If, Though, Even if, Even though, In order that, Since, Though, , After, Although, Before, So that, Until, Where, Than, Unless, When, While |
| Correlative Conjunctions | These conjunctions connect similar word groups, working in pairs within a sentence. Common correlative conjunctions are below: | Whether / Or, Both / And, Not only, But also, As/ As, Neither / Nor, Either / Or, Just / So, The more/ The more, No sooner / Than, Rather / Than |
Conjunctions, its types with Definitions and Examples