Can you even count how many sentences you hear or say each day? Too many right? There are 4 Types of Sentences. How we can categorize sentences based on their structure and function? Let’s explore Types of Sentence with Sentence Structure and Example.
A definition of Sentence:
To excel in our communication, we need a structured group of words arranged in a particular order. A sentence can be defined as a group of words that includes a subject and a verb, resulting in a complete statement or question. Today, we will explore Kinds of Sentence, and sentence structures with examples and punctuation.
Examples of Sentence Structures:
- She(Subject) went(Verb).
- She (Subject) finished(V) her thesis(Object).
- They (Subject) researched(Verb) Probiotics (Object) for many hours (Prepositional Phrases).
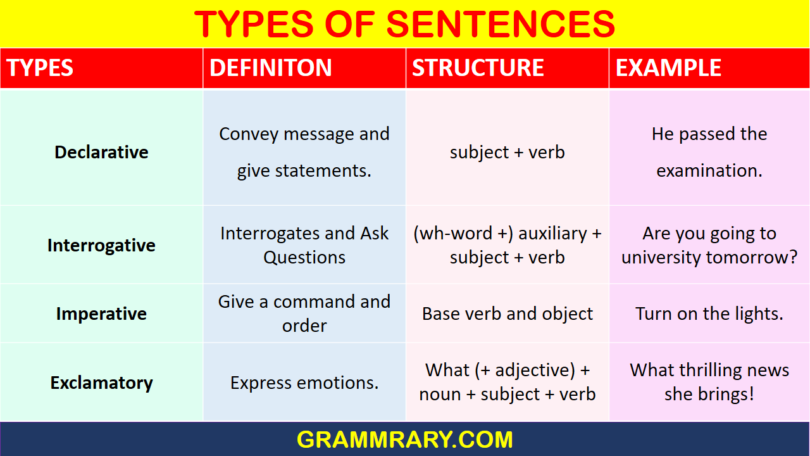
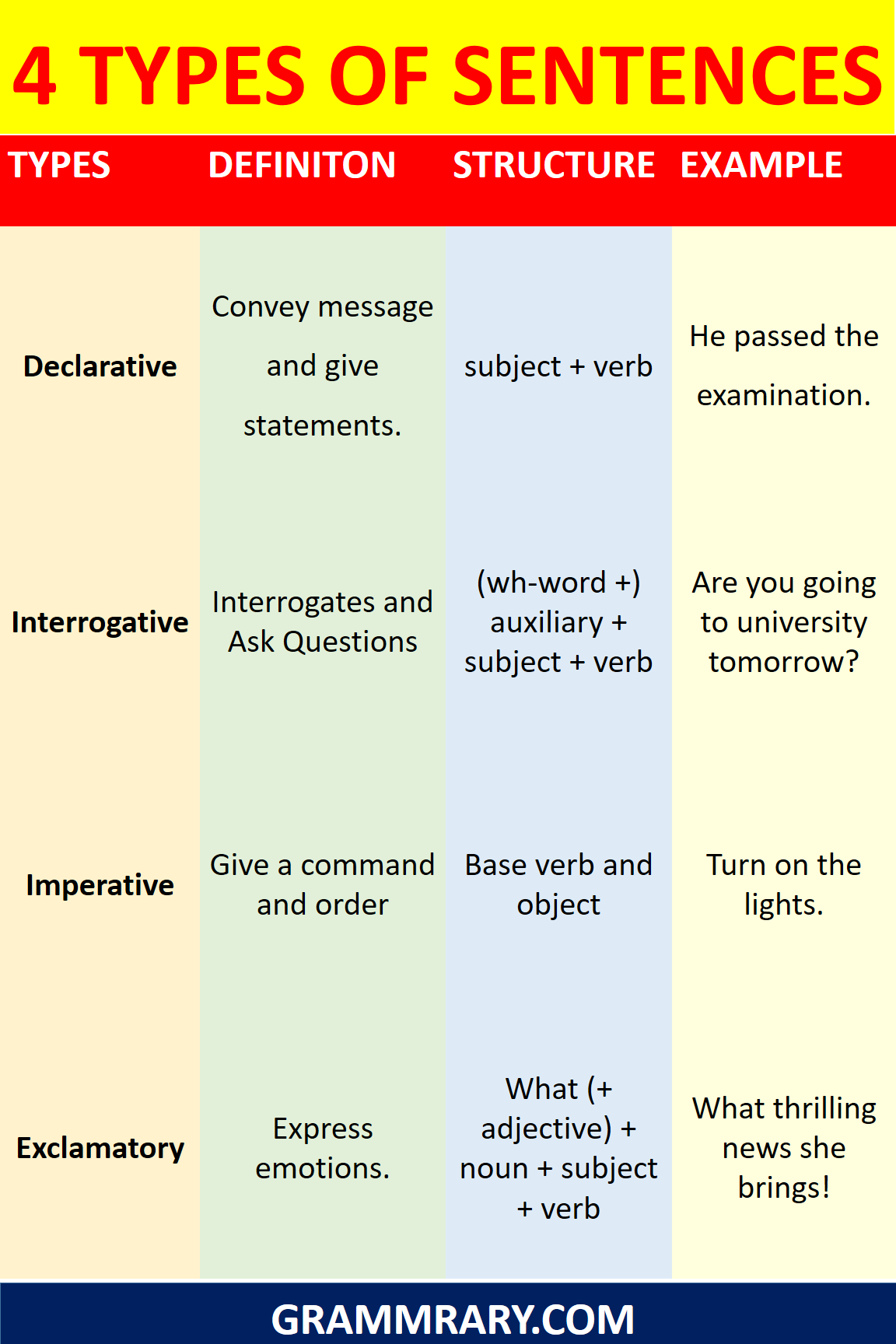
4 types of sentences with Examples:
- declarative sentence (statement)
- interrogative sentence (question)
- imperative sentence (command)
- exclamative sentence (exclamation)
| Types of Sentence | Objective of Sentence | Punctuation Mark |
| Declarative | To convey a message or give a statement. | Ends with a Full Stop (.) |
| Interrogative | It asks questions. | It ends with a Question mark (?) |
| Imperative | It is used to request, give a command or an order. | It ends with a Full stop (.) |
| Exclamatory | To express emotions. | Ends with an Exclamation mark (!) |
Four Types of Sentences with Examples and Structures:
Definition of Declarative Sentence:
Declarative Sentences convey a message, inform about a decision, or give a statement. They usually end with a period.
Sentence Structure of Declarative Sentence:
subject + verb
Example Sentences of Declarative Sentence:
- She loves to travel to different countries.
- This book is amazing.
Positive and negative Examples of Declarative sentences:
| Positive | Negative |
|---|---|
| I like Tea. | I don’t like tea. |
| We went outside last night. | We did not went outside last night. |
| He passed the examination. | He did not pass the examination. |
| She is baking cakes. | She is not baking cakes. |
| Lisa sings beautifully. | Lisa does not sings beautifully. |
Interrogative Sentence:
Its dynamic feature is to interrogate about something or to ask questions. It ends with a question mark.
Shayari began long ago in Urdu literature and has roots reaching back centuries. It draws heavily from Persian poetry, which influenced Indian poets. Over time, it merged with Indian traditions, creating a unique blend. Historically, shayari was not only for entertainment but also used to comment on society and promote change.
Sentence Structure:
(wh-word +) auxiliary + subject + verb
Interrogative Sentences are further classified into Positive and Negative sentences.
Interrogative Sentences Examples:
- Are you going to university tomorrow?
- What is the venue of the meeting?
- Where are you going on vacation?
The 3-main types of questions Interrogative Sentences cover:
- Choice question
- WH- word question
- Yes/No question
Interrogative sentences can be positive or negative. Look at these examples
| Positive | Negative |
|---|---|
| Do you like Tea? | Don’t you like Tea? |
| Are you feeling better today? | Aren’t you feeling better today? |
| Why did you buy this shirt? | Why didn’t you buy this shirt? |
| Are you going to attend the Annual Dinner? | Aren’t you going to attend the Annual Dinner? |
| Are you feeling tired? | Aren’t you feeling tired? |
Imperative Sentence:
Imperative sentences give instructions or commands. It doesn’t necessarily need a subject for a complete meaning or appropriate structure. They may only include a verb or an object and end with a period (.) or exclamation mark (!).
Sentence Structure:
Base verb and object
The subject is not compulsory because the subject is a reader or listener.
Imperative Sentences Examples:
- Shut the door when you go out.
- Bring ice cream after dinner.
- Turn on the lights.
Imperative Sentences are further categorized into positive or negative sentences.
| Positive | Negative |
|---|---|
| Buy this Shirt. | Don’t buy this shirt. |
| Hold it! | Don’t go outside. |
| Lock your room while going out. | Don’t lock your room from the inside. |
| Bring the flowers when you are back. | Don’t misbehave with others. |
| Give me a piece of cake. | Don’t give me a piece of cake. |
Exclamative Sentence:
These show strong emotion or surprise. It ends with an exclamation mark (!).
Sentence Structure:
What (+ adjective) + noun + subject + verb
How (+ adjective/adverb) + subject + verb
Exclamatory Sentences Examples:
- What a cheater she is!
- What thrilling news she brings!
- How he behaved!
Positive and Negative Exclamatory Sentences:
| Positive | Negative |
| What a beautiful shirt you got! | What a horror movie this is! |
| How tasty this pasta is! | How disappointing your results are! |
| Wow, you did an outstanding work! | Oh no, I forgot my wallet at home! |
| What an outstanding result this is! | What a waste of money and time you did! |
| Wow, how beautiful these flowers are! | How hectic it is to deal with him! |
4 Types of Sentence with Definitons, Examples and Sentence Structures
Types of Sentences Based on Structure
After exploring the classification of sentences on the basis of function, let’s proceed to The Types of Sentences on the basis of Structure.
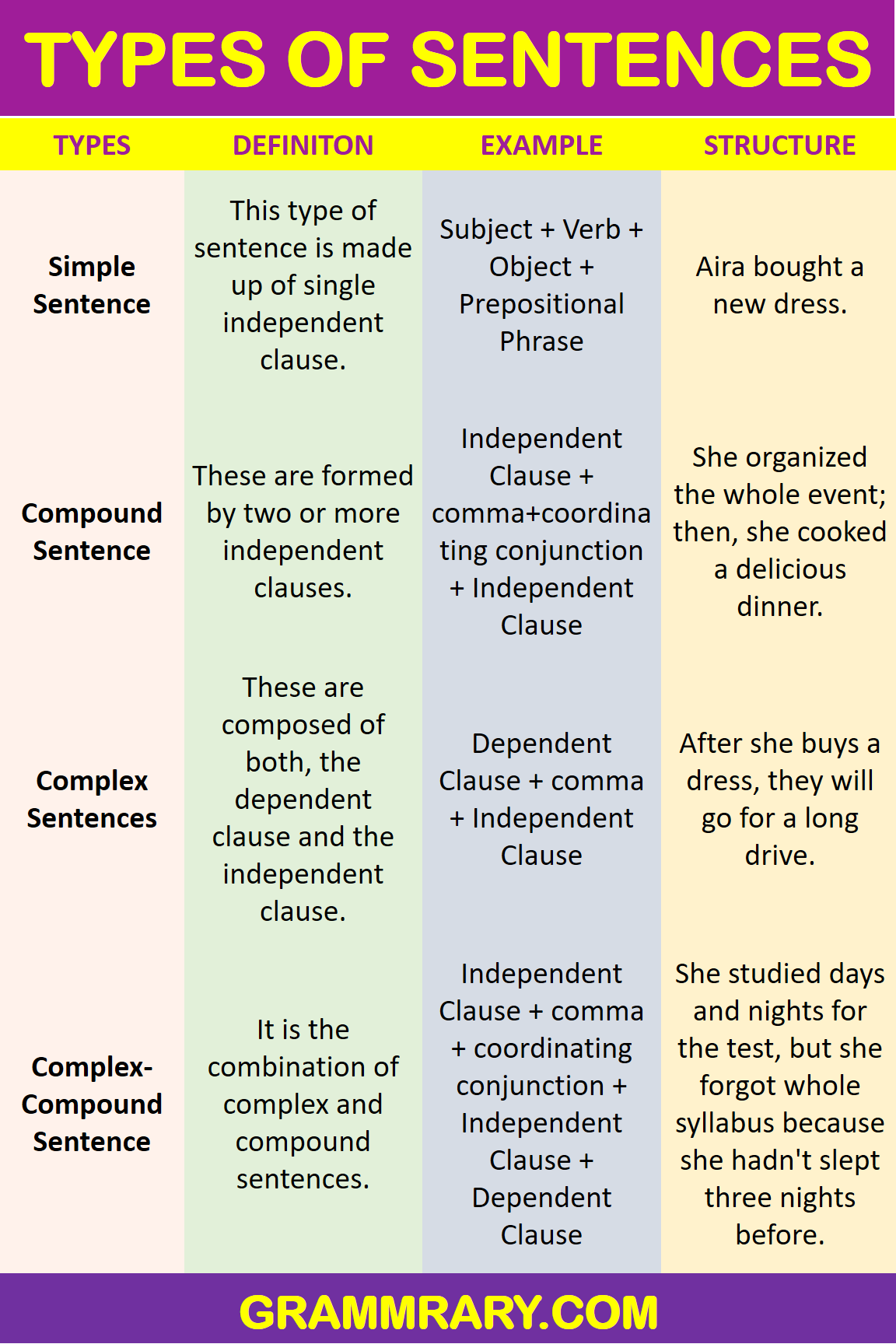
Here are 4-types of sentences based on sentence structures:
Simple Sentence:
This type of sentence is made up of single independent clause. It includes a subject and tells about an action happening along with the subject.Besides a subject, it contains a predicate. A predicate is a verb phrase or verb and describes the action the subject performs. Simple sentence can include one or more verbs.
Composed of:
Single Independent Clause
Simple Sentence Structure:
Subject + Verb + Object + Prepositional Phrase
- I (Subject) like (Verb) coffee (Object).
- They (Subject) learn (Verb) Science lessons (Object) for many hours (Prepositional Phrase)
For Example,
- Aira bought a new dress.
- Aman is doing his thesis.
Compound sentences
These are formed by two or more independent clauses. The independent clauses are linked together by a conjunctive adverb, linking word, conjunction, or semicolon. The coordinating conjunctions include nor, are, or, and, but, for, yet, etc. Some examples of Conjunctive adverbs are likewise, therefore, rather, etc.
Composed of:
Two or more independent clauses linked together by a conjunctive adverb, linking word, semicolon, or conjunction.
Compound Sentence Structure:
Independent Clause + comma+coordinating conjunction + Independent Clause
Independent Clause + Dependent Clause
- Because he scheduled his routine (Independent Clause), (comma) it was easier for him to manage all tasks in time (Dependent Clause).
For Example,
- She finished her research article, and she finalized the references.
- She organized the whole event; then, she cooked a delicious dinner.
These are composed of both, the dependent clause and the independent clause. There is one independent clause and one or more dependent clauses. These clauses are joined together by subordinating conjunctions or Relative Pronouns. The Subordinating conjunctions include after, when, because, etc. The examples of relative pronouns are which, who, that, etc. A comma can connect clauses if the dependent clause comes first in the sentence. A simple comma will connect the clauses when the dependent clause appears first in the sentence.
Composed of:
One independent clause + one or more dependent clauses joined by subordinating conjunctions or Relative Pronouns.
Complex Sentence Structure:
Dependent Clause + comma + Independent Clause
Independent Clause + Dependent Clause
- He completed his review (Independent Clause), and (coordinating conjunction) he concluded the topic (independent clause).
For example:
- After she buys a dress, they will go for a long drive.
- She gave us a party because she got a distinction in university.
Complex-Compound sentences
Complex-compound Sentences are the combination of complex and compound sentences. It is formed of both, dependent and independent clauses. There is one or more dependent clauses and a minimum of two independent clauses. These are linked with coordinating conjunctions, with a comma just behind coordinating conjunctions.
Composed of:
One or more dependent clauses + two or more independent clauses joined by coordinating conjunctions.
Complex-Compound Sentence Structure:
Independent Clause + comma + coordinating conjunction + Independent Clause + Dependent Clause
Dependent Clause + comma + Independent Clause + Comma + Coordinating Conjunction + Independent Clause.
- Although he organized his schedule ( Dependent Clause) , (Comma) he decided to reschedule his tasks (Independent Clause) , (Comma) and (Coordinating Conjunction) he carefully analyzed and plan the day (INdepedent Clause).
For example:
- After she went to the park, the girl, who is beautiful and smart and wears a black maxi, goes shopping, had an accident, and got severely injured.
- She studied days and nights for the test, but she forgot whole syllabus because she hadn’t slept three nights before.
Tabular Representation:
| TYPES OF SENTENCE | DEFINITION | STRUCTURE | EXAMPLE |
| Simple Sentence | This type of sentence is made up of single independent clause. | Subject + Verb + Object + Prepositional Phrase | Aira bought a new dress. |
| Compound Sentence | These are formed by two or more independent clauses. | Independent Clause + comma+coordinating conjunction + Independent Clause | She organized the whole event; then, she cooked a delicious dinner. |
| Complex Sentences | These are composed of both, the dependent clause and the independent clause. | Dependent Clause + comma + Independent Clause | After she buys a dress, they will go for a long drive. |
| Complex-Compound Sentence | It is the combination of complex and compound sentences. | Independent Clause + comma + coordinating conjunction + Independent Clause + Dependent Clause | After she went to the park, the girl, who is beautiful and smart and wears a black maxi, goes shopping, had an accident, and got severely injured. |
4 Types of Sentence with Definitons, Examples and Sentence Structures